Create a vector RAG chatbot
This tutorial demonstrates how you can use Robility flow to create a chatbot application that uses Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to embed your data as vectors in a vector database and then chat with the data.
Prerequisites
a. Create a Robility flow API key
b. Create an OpenAI API key
c. Install the Robility flow JavaScript client
d. Be familiar with vector search concepts and applications, such as vector databases and RAG.
Create a vector RAG flow
1. In Robility flow, click New Flow, and then select the Vector Store RAG template.
About the Vector Store RAG template:
This template has two flows.
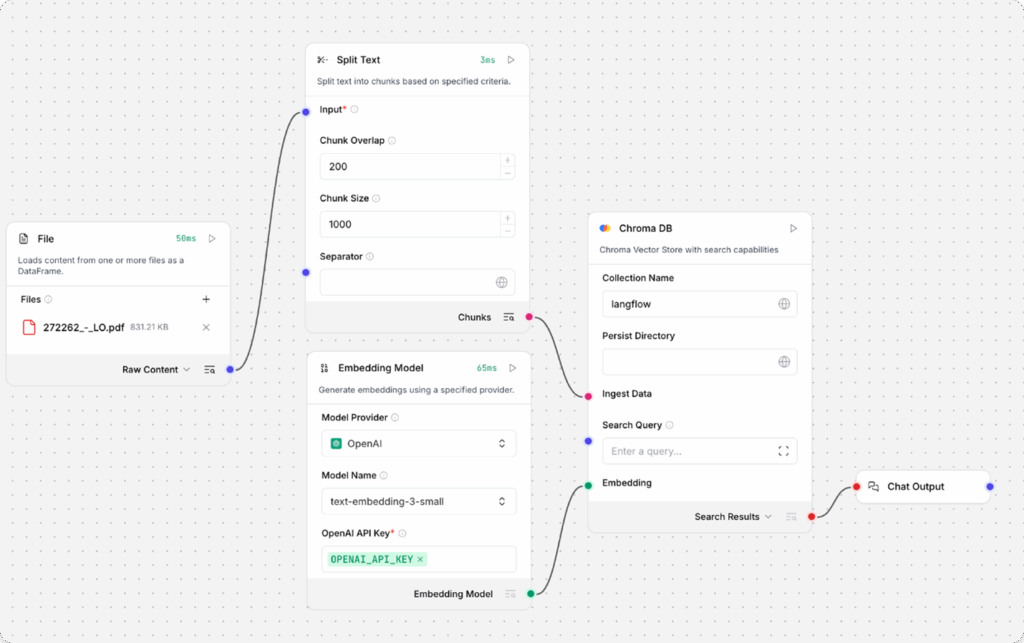
The Load Data Flow populates a vector store with data from a file. This data is used to respond to queries submitted to the Retriever Flow.
Specifically, the Load Data Flow ingests data from a local file, splits the data into chunks, loads and indexes the data in your vector database, and then computes embeddings for the chunks. The embeddings are also stored with the loaded data. This flow only needs to run when you need to load data into your vector database.
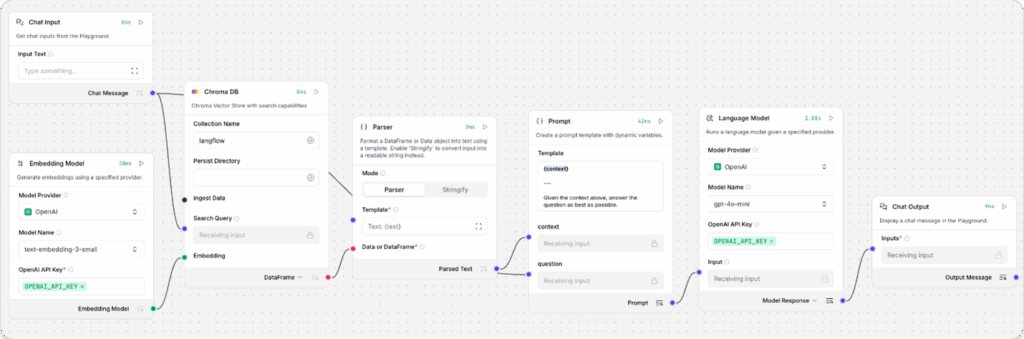
The Retriever Flow receives chat input, generates an embedding for the input, and then uses several components to reconstruct chunks into text and generate a response by comparing the new embedding to the stored embeddings to find similar data.
2. Add your OpenAI API key to OpenAI Embeddings components.
3. Optional: Replace both Astra DB vector store components with a Chroma DB or another Vector Store component of your choice. This tutorial uses Chroma DB.
The Load Data Flow should have File, Split Text, Embedding Model, vector store (such as Chroma DB), and Chat Output components:
The Retriever Flow should have Chat Input, Embedding Model, vector store, Parser, Prompt, Language Model, and Chat Output components:
The flows are ready to use. Continue the tutorial to learn how to use the loading flow to load data into your vector store and then call the chat flow in a chatbot application.
Load data and generate embeddings
To load data and generate embeddings, you can use the visual editor or the /v2/files endpoint.
The visual editor option is simpler, but it is only recommended for scenarios where the user who created the flow is the same user who loads data into the database.
In situations where many users load data or you need to load data programmatically, use the Robility flow API option.
a. Visual editor
b. Robility flow API
1. In your RAG chatbot flow, click the File component, and then click File.
2. Select the local file you want to upload, and then click Open. The file is loaded to your Robility flow server.
3. To load the data into your vector store, click the Vector Store component, and then click Run component to run the selected component and all prior dependent components.
When the flow runs, the flow ingests the selected file, chunks the data, loads the data into the vector store database, and then generates embeddings for the chunks, which are also stored in the vector store.
Your database now contains data with vector embeddings that an LLM can use as context to respond to queries, as demonstrated in the next section of the tutorial.
Chat with your flow from a JavaScript application
To chat with the data in your vector database, create a chatbot application that runs the Retriever Flow programmatically.
This tutorial uses JavaScript for demonstration purposes.
1. To construct the chatbot, gather the following information:
a. ROBILITY FLOW _SERVER_ADDRESS: Your Robility flow server’s domain. The default value is 127.0.0.1:7860. You can get this value from the code snippets on your flow’s API access pane.
b. FLOW_ID: Your flow’s UUID or custom endpoint name. You can get this value from the code snippets on your flow’s API access pane.
c. ROBILITY FLOW _API_KEY: A valid Robility flow API key.
2. Copy the following script into a JavaScript file, and then replace the placeholders with the information you gathered in the previous step:
const readline = require(‘readline’);
const { Robility flow Client } = require(‘@datastax/Robility flow -client’);
const API_KEY = ‘ROBILITY FLOW _API_KEY’;
const SERVER = ‘ROBILITY FLOW _SERVER_ADDRESS’;
const FLOW_ID = ‘FLOW_ID’;
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input: process.stdin, output: process.stdout });
// Initialize the Robility flow client
const client = new Robility flow Client({
baseUrl: SERVER,
apiKey: API_KEY
});
async function sendMessage(message) {
try {
const response = await client.flow(FLOW_ID).run(message, {
session_id: ‘user_1’
});
// Use the convenience method to get the chat output text
return response.chatOutputText() || ‘No response’;
} catch (error) {
return `Error: ${error.message}`;
}
}
function chat() {
console.log(‘🤖 Robility flow RAG Chatbot (type “quit” to exit)\n’);
const ask = () => {
rl.question(‘👤 You: ‘, async (input) => {
if ([‘quit’, ‘exit’, ‘bye’].includes(input.trim().toLowerCase())) {
console.log(‘👋 Goodbye!’);
rl.close();
return;
}
const response = await sendMessage(input.trim());
console.log(`🤖 Assistant: ${response}\n`);
ask();
});
};
ask();
}
chat();
The script creates a Node application that chats with the content in your vector database, using the chat input and output types to communicate with your flow. Chat maintains ongoing conversation context across multiple messages. If you used text type inputs and outputs, each request is a standalone text string.
3. Save and run the script to send the requests and test the flow.
Result
The following is an example response from this tutorial’s flow. Due to the nature of LLMs and variations in your inputs, your response might be different.
👤 You: Do you have any documents about engines?
🤖 Assistant: Yes, the provided text contains several warnings and guidelines related to engine installation, maintenance, and selection. It emphasizes the importance of using the correct engine for specific applications, ensuring all components are in good condition, and following safety precautions to prevent fire or explosion. If you need more specific information or details, please let me know!
👤 You: It should be about a Briggs and Stratton engine.
🤖 Assistant: The text provides important safety and installation guidelines for Briggs & Stratton engines. It emphasizes that these engines should not be used on 3-wheel All-Terrain Vehicles (ATVs), motor bikes, aircraft products, or vehicles intended for competitive events, as such uses are not approved by Briggs & Stratton.
If you have any specific questions about Briggs & Stratton engines or need further information, feel free to ask!