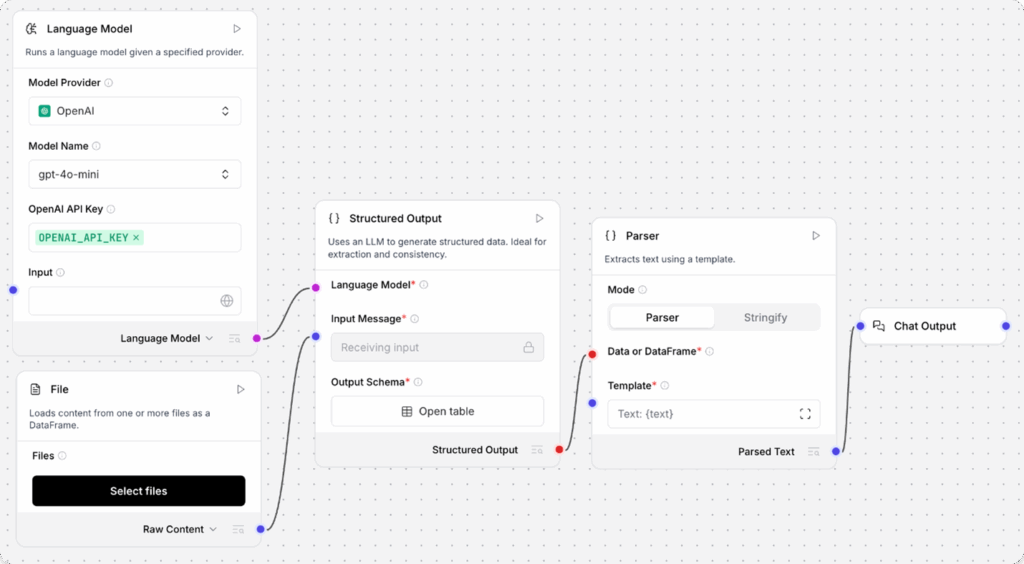
Parser
The Parser component extracts text from structured data (DataFrame or Data) using a template or direct stringification. The output is a Message containing the parsed text.
This is a versatile component for data extraction and manipulation in your flows. For examples of Parser components in flows, see the following:
1. Batch Run component
2. Structured Output component
3. Financial Report Parser template
4. Vector Store components
5. Trigger flows with webhooks
6. Create a vector RAG chatbot
Parsing modes
The Parser component has two modes: Parser and Stringify.
Parser (template) mode
In Parser mode, you create a template for text output that can include literal strings and variables for extracted keys.
Use curly braces to define variables anywhere in the template. Variables must match keys in the DataFrame or Data input, such as column names. For example, {name} extracts the value of a name key. For more information about the content and structure of DataFrame and Data objects, see Robility flow data types.
When the flow runs, the Parser component iterates over the input, producing a Message for each parsed item. For example, parsing a DataFrame creates a Message for each row, populated with the unique values from that row.
Employee summary template
This example templates extracting employee data into a natural language summary about an employee’s hire date and current role:
{employee_first_name} {employee_last_name} was hired on {start_date}.
Their current position is {job_title} ({grade}).
The resulting Message output replaces the variables with the corresponding extracted values. For example:
Renlo Kai was hired on 11-July-2017.
Their current position is Software Engineer (Principal).
Employee profile template
This example template uses Markdown syntax and extracted employee data to create an employee profile:
# Employee Profile
When the flow runs, the Parser component iterates over each row of the DataFrame, populating the template’s variables with the appropriate extracted values. The resulting text for each row is output as a Message.
Stringify mode
Use Stringify mode to convert the entire input directly to text. This mode doesn’t support templates or key selection.
The following parameters are available in Parser mode. To view and edit all available parameters, click Controls in the component’s header menu.
| Name | Display Name | Info |
|---|---|---|
| input_data | Data or DataFrame | Input parameter. The Data or DataFrame input to parse. |
| pattern | Template | Input parameter. The formatting template using plaintext and variables for keys ({KEY_NAME}). See the preceding examples for more information. |
| sep | Separator | Input parameter. A string defining the separator for rows or lines. Default: \n (new line). |
| clean_data | Clean Data | Whether to remove empty rows and lines in each cell or key of the DataFrame or Data input. Default: Enabled (true) |
Test and troubleshoot parsed text
To test the Parser component, click Run component, and then click Inspect output to see the Message output with the parsed text. You can also connect a Chat Output component if you want to view the output in the Playground.
If the Message output from the Parser component has empty or unexpected values, there might be a mapping error between the input and the parsing mode, the input has empty values, or the input isn’t suitable for plaintext extraction.
For example, assume you use the following template to parse a DataFrame:
{employee_first_name} {employee_last_name} is a {job_title} ({grade}).
The following Message could result from parsing a row where employee_first_name was empty and grade was null:
Smith is a Software Engineer (null).
To troubleshoot missing or unexpected values, you can do the following:
1. Make sure the variables in your template map to keys in the incoming Data or DataFrame. To see the data being passed directly to the Parser component, click Inspect output on the component that is sending data to the Parser component.
2. Check the source data for missing or incorrect values. There are several ways you can address these inconsistencies:
a. Rectify the source data directly.
b. Use other components to amend or filter anomalies before passing the data to the Parser component. There are many components you can use for this depending on your goal, such as the Data Operations, Structured Output, and Smart Function components.
Enable the Parser component’s Clean Data parameter to skip empty rows or lines.